数据出入
In Elasticsearch, all data in every field is indexed by default. That is, every field has a dedicated inverted index for fast retrieval. And, unlike most other databases, it can use all of those inverted indices in the same query, to return results at breathtaking speed.
文档格式
{
"name": "John Smith",
"age": 42,
"confirmed": true,
"join_date": "2014-06-01",
"home": {
"lat": 51.5,
"lon": 0.1
},
"accounts": [
{
"type": "facebook",
"id": "johnsmith"
},
{
"type": "twitter",
"id": "johnsmith"
}
]
}
Warning: Field names can be any valid string, but may not include periods.
每个文档包含了三个元数据:
_index: Where the document lives_type: The class of object that the document represents_id: The unique identifier for the document
存储文档
PUT /{index}/{type}/{id}
{
"field": "value",
...
}
举例:
PUT /website/blog/123
{
"title": "My first blog entry",
"text": "Just trying this out...",
"date": "2014/01/01"
}
{
"_index": "website",
"_type": "blog",
"_id": "123",
"_version": 1,
"created": true
}
每个文档都有一个版本号,每次修改或删除文档时,_version就会自增。
如果不提供ID,就会随机产生一个ID。但是注意,必须用POST(“store this document under this URL”)方法代替PUT(“store this document at this URL”)方法。
POST /website/blog/
{
"title": "My second blog entry",
"text": "Still trying this out...",
"date": "2014/01/01"
}
{
"_index": "website",
"_type": "blog",
"_id": "AVFgSgVHUP18jI2wRx0w",
"_version": 1,
"created": true
}
Autogenerated IDs are 20 character long, URL-safe, Base64-encoded GUID strings. These GUIDs are generated from a modified FlakeID scheme which allows multiple nodes to be generating unique IDs in parallel with essentially zero chance of collision.
读取文档
使用GET方法即可读取一个指定ID的文档,追加?pretty参数可以美化json输出。如果没有找到文档,将会返回404。可以通过curl -i参数打印出服务器的响应头:
curl -i -XGET http://localhost:9200/website/blog/124?pretty
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8
Content-Length: 83
{
"_index" : "website",
"_type" : "blog",
"_id" : "124",
"found" : false
}
默认情况下GET会返回整个文档,存储在_source字段下。如果只想返回指定的部分字段,可以像这样:
GET /website/blog/123?_source=title,text
{
"_index" : "website",
"_type" : "blog",
"_id" : "123",
"_version" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"title": "My first blog entry" ,
"text": "Just trying this out..."
}
}
如果只想显示_source,忽略元数据字段,可以像这样:
GET /website/blog/123/_source
{
"title": "My first blog entry",
"text": "Just trying this out...",
"date": "2014/01/01"
}
检测文档是否存在
使用HEAD方法即可:
curl -i -XHEAD http://localhost:9200/website/blog/123
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Content-Length: 0
curl -i -XHEAD http://localhost:9200/website/blog/124
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Content-Length: 0
更新整个文档
ES中存储的文档是不可变的,无法只更新文档的部分字段,必须reindex或replace。
使用indexAPI即可完成replace:
PUT /website/blog/123
{
"title": "My first blog entry",
"text": "I am starting to get the hang of this...",
"date": "2014/01/02"
}
{
"_index" : "website",
"_type" : "blog",
"_id" : "123",
"_version" : 2,
"created": false
}
_version字段自增,created为false,因为之前这个ID已经存在了。
在内部,ES会对旧文档标记为删除,并添加了整个新文档。但是旧文档不会立刻被清理掉,你也无法访问到。ES会在后台清理掉文档。
后面会提到一个updateAPI,看起来是部分替换了文档。但实际上还是遵从前面提到的原则:
- Retrieve the JSON from the old document
- Change it
- Delete the old document
- Index a new document
不同的是update通过客户端一次请求实现,而不是分开GET和index请求。
创建新文档
想要确保创建一个新文档而不是覆盖已有的文档,最简单的方法是使用POST方法不指定ID:
POST /website/blog/
{ ... }
如果必须要指定_id的话,使用op_type query string或/_createendpoint:
PUT /website/blog/123?op_type=create
{ ... }
PUT /website/blog/123/_create
{ ... }
如果成功创建,返回201 created,否则返回409 Conflict。
删除文档
DELETE /website/blog/123
如果找到文档,返回200 OK,响应body中_version增加1:
{
"found" : true,
"_index" : "website",
"_type" : "blog",
"_id" : "123",
"_version" : 3
}
找不到就返回404 Not Found,_version也不会增加:
{
"found" : false,
"_index" : "website",
"_type" : "blog",
"_id" : "123",
"_version" : 4
}
处理冲突
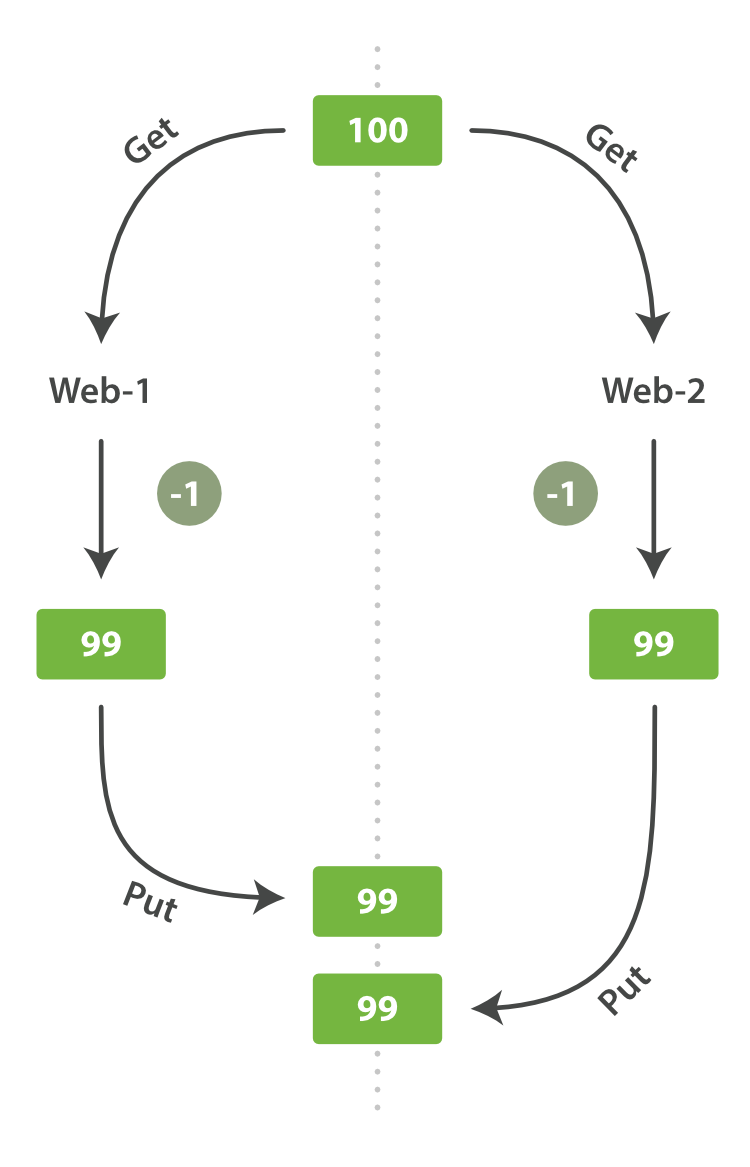
这种情况在关系型数据库中称为不可重复读。在大多数ES场景中无需关心——因为用作关系型数据库的缓存,基本上只会插入数据,几乎不会修改数据。
但是如果需要处理这种冲突的场景时,可以按照以下方案解决:
- 悲观并发控制(Pessimistic concurrency control): 关系型数据库常用。假定冲突修改随时可能发生,因此每次修改需要锁定资源.典型的例子就是读取前锁定一行数据,确保只有一个线程能修改这一行的数据
- 乐观并发控制(Optimistic concurrency control): ES使用这种方法。假定冲突不太可能发生,因此并不阻止更新操作。如果在读写间数据发生了修改,那么更新就会失败,交由应用程序自己处理冲突。如刷新数据后重试,或者给用户反馈情况。
乐观并发控制
每个文档都有一个_version元数据,存储着文档的修改次数。可以利用这个属性确保修改是由应用程序本身修改的。
PUT /website/blog/1/_create
{
"title": "My first blog entry",
"text": "Just trying this out..."
}
GET /website/blog/1
{
"_index" : "website",
"_type" : "blog",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"title": "My first blog entry",
"text": "Just trying this out..."
}
}
PUT /website/blog/1?version=1
{
"title": "My first blog entry",
"text": "Starting to get the hang of this..."
}
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "version_conflict_engine_exception",
"reason": "[blog][1]: version conflict, current [2], provided [1]",
"index": "website",
"shard": "3"
}
],
"type": "version_conflict_engine_exception",
"reason": "[blog][1]: version conflict, current [2], provided [1]",
"index": "website",
"shard": "3"
},
"status": 409
}
如果版本是由外部系统管理的,可以追加version_type=external这个query string。
PUT /website/blog/2?version=5&version_type=external
部分更新文档
前面提到过一个update方法:
POST /website/blog/1/_update
{
"doc" : {
"tags" : [ "testing" ],
"views": 0
}
}
返回:
{
"_index" : "website",
"_id" : "1",
"_type" : "blog",
"_version" : 3
}
取出的时候可以看到结果:
{
"_index": "website",
"_type": "blog",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 3,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"title": "My first blog entry",
"text": "Starting to get the hang of this...",
"tags": [ "testing" ],
"views": 0
}
}
使用脚本实现部分更新
POST /website/blog/1/_update
{
"script" : "ctx._source.views+=1"
}
Scripts can be used in the update API to change the contents of the _source field, which is referred to inside an update script as ctx._source.
Scripting with Groovy
ES允许嵌入自己的逻辑脚本,很多API都支持脚本。脚本可以从一个特殊的.script索引中取出,或从磁盘读取。
默认的脚本语言是Groovy,处于关闭状态。你还可以通过在所有集群节点设置
script.groovy.sandbox.enabled: false
关闭沙箱,就可以从.scripts索引和config/scripts/目录读取脚本。
更多脚本的内容: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/modules-scripting.html
POST /website/blog/1/_update
{
"script" : "ctx._source.tags+=new_tag",
"params" : {
"new_tag" : "search"
}
}
{
"_index": "website",
"_type": "blog",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 5,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"title": "My first blog entry",
"text": "Starting to get the hang of this...",
"tags": ["testing", "search"],
"views": 1
}
}
还可以基于文档本身内容进行删除操作,通过设置ctx.op为delete:
POST /website/blog/1/_update
{
"script" : "ctx.op = ctx._source.views == count ? 'delete' : 'none'",
"params" : {
"count": 1
}
}
更新可能不存在的文档
假设要更新页面计数器,对于新页面可能不存在这个计数器,那么更新可能会失败。
此时我们需要upsert操作:
POST /website/pageviews/1/_update
{
"script" : "ctx._source.views+=1",
"upsert": {
"views": 1
}
}
如果要避免更新冲突,可以利用_version字段,追加retry_on_conflict参数:
POST /website/pageviews/1/_update?retry_on_conflict=5
{
"script" : "ctx._source.views+=1",
"upsert": {
"views": 0
}
}
取出多个文档
如果需要一次从ES取出多个文档,可以使用mgetAPI。mget期望一个docs数组参数,每个元素包含_index, _type, 和_id元数据,还可以指定_source参数指定需要返回的字段。
GET /_mget
{
"docs" : [
{
"_index" : "website",
"_type" : "blog",
"_id" : 2
},
{
"_index" : "website",
"_type" : "pageviews",
"_id" : 1,
"_source": "views"
}
]
}
响应主体会包含一个docs数组:
{
"docs" : [
{
"_index" : "website",
"_id" : "2",
"_type" : "blog",
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"text" : "This is a piece of cake...",
"title" : "My first external blog entry"
},
"_version" : 10
},
{
"_index" : "website",
"_id" : "1",
"_type" : "pageviews",
"found" : true,
"_version" : 2,
"_source" : {
"views" : 2
}
}
]
}
还可以在URL上确定默认的_index和_type:
GET /website/blog/_mget
{
"docs" : [
{ "_id" : 2 },
{ "_type" : "pageviews", "_id" : 1 }
]
}
如果所有的文档都在同一个_index,_type,可以直接指定一个ids数组:
GET /website/blog/_mget
{
"ids" : [ "2", "1" ]
}
不包含ID2的文档 ,响应如下:
{
"docs" : [
{
"_index" : "website",
"_type" : "blog",
"_id" : "2",
"_version" : 10,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"title": "My first external blog entry",
"text": "This is a piece of cake..."
}
},
{
"_index" : "website",
"_type" : "blog",
"_id" : "1",
"found" : false
}
]
}
NOTE:
mget总会返回200,即使一个文档也没找到。因为mget本身的请求是成功的
bulk操作
_mget只能一次性取出多条文档,但是bulkAPI允许一次请求处理多个create, index, update, 或delete操作。
bulk请求的body格式:
{ action: { metadata }}\n
{ request body }\n
{ action: { metadata }}\n
{ request body }\n
...
就像是合法的json line通过换行符(\n)连接到一起,需要注意两点:
- Every line must end with a newline character (
\n), including the last line. These are used as markers to allow for efficient line separation. - The lines cannot contain unescaped newline characters, as they would interfere with parsing. This means that the JSON must not be pretty-printed.
action/metadata行指明对哪个文档执行执行什么操作
action必须为以下之一:
createindexupdatedelete
metadata需要指明_index, _type, 和_id。
{ "delete": { "_index": "website", "_type": "blog", "_id": "123" }}
request body行被index和create操作依赖时,由_source本身构成。由update操作依赖时,doc, upsert, script, and so forth。对于delete无需这一行。
{ "create": { "_index": "website", "_type": "blog", "_id": "123" }}
{ "title": "My first blog post" }
不指定ID时,自动生成:
{ "index": { "_index": "website", "_type": "blog" }}
{ "title": "My second blog post" }
合在一起:
POST /_bulk
{ "delete": { "_index": "website", "_type": "blog", "_id": "123" }}
{ "create": { "_index": "website", "_type": "blog", "_id": "123" }}
{ "title": "My first blog post" }
{ "index": { "_index": "website", "_type": "blog" }}
{ "title": "My second blog post" }
{ "update": { "_index": "website", "_type": "blog", "_id": "123", "_retry_on_conflict" : 3} }
{ "doc" : {"title" : "My updated blog post"} }
特别注意不要少了最后一行的换行符。
ES的响应会放在items数组,按照bulk请求的顺序。
{
"took": 4,
"errors": false,
"items": [
{ "delete": {
"_index": "website",
"_type": "blog",
"_id": "123",
"_version": 2,
"status": 200,
"found": true
}},
{ "create": {
"_index": "website",
"_type": "blog",
"_id": "123",
"_version": 3,
"status": 201
}},
{ "create": {
"_index": "website",
"_type": "blog",
"_id": "EiwfApScQiiy7TIKFxRCTw",
"_version": 1,
"status": 201
}},
{ "update": {
"_index": "website",
"_type": "blog",
"_id": "123",
"_version": 4,
"status": 200
}}
]
}
每个操作独立执行,不会影响其他操作。如果任意一个操作失败了,顶级errors会被设置为true。
POST /_bulk
{ "create": { "_index": "website", "_type": "blog", "_id": "123" }}
{ "title": "Cannot create - it already exists" }
{ "index": { "_index": "website", "_type": "blog", "_id": "123" }}
{ "title": "But we can update it" }
{
"took": 3,
"errors": true,
"items": [
{ "create": {
"_index": "website",
"_type": "blog",
"_id": "123",
"status": 409,
"error": "DocumentAlreadyExistsException
[[website][4] [blog][123]:
document already exists]"
}},
{ "index": {
"_index": "website",
"_type": "blog",
"_id": "123",
"_version": 5,
"status": 200
}}
]
}
这同样意味着bulk操作非原子性: 不能用于实现交易。
不要重复自己
对同样的_index同样的_type批量操作时,可以仿照_mget那样,指定默认的_index和_type:
POST /website/_bulk
{ "index": { "_type": "log" }}
{ "event": "User logged in" }
依然可以覆盖掉默认的_index和_type参数:
POST /website/log/_bulk
{ "index": {}}
{ "event": "User logged in" }
{ "index": { "_type": "blog" }}
{ "title": "Overriding the default type" }
多大的数据量算大
整个bulk请求会加载到内存中,因此bulk操作受限于硬件环境。
一般一批文档数量是1000 - 5000,根据每个文档大小调整。
关注物理内存消耗也很有用,一个好的bulk size通常是5 - 15MB。